What is a TFCC injury?
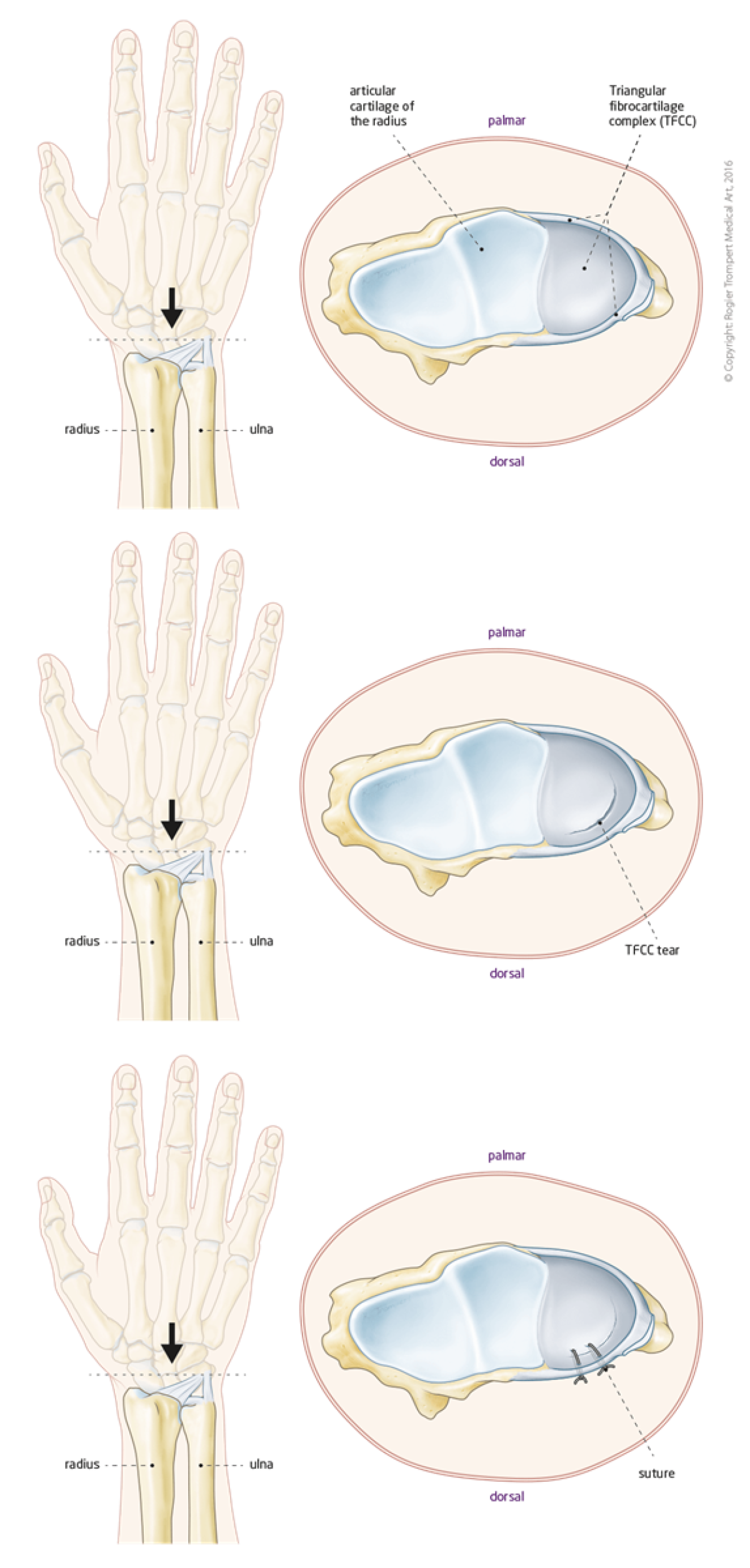
The two forearm bones are the ulna and the radius. When one rotates the forearm the radius rotates over the ulna at the wrist at the DRU joint. Stability of this joint is provided by the TFCC (Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex).
The TFCC can become weak after injury (tear) or overuse. This typically cases pain at the wrist on the side of the little finger. Also the DRU joint can become unstable causing weakness, pain and reduced range of motion.
Diagnosis & treatment of a TFCC injury
History and physical examination by a hand / wrist surgeon are the foundation of the diagnosis, but additional tests will be required. X-rays and an MRI or CT scan are very useful to confirm the diagnosis.
If needed, a wrist arthroscopy can be considered. This is the best way to establish the severity and exact location of the TFCC injury. During this procedure the surgeon can see inside the wrist using four small incisions (+/- 5 mm each) and a fibre-optic camera.
Once the diagnosis and its severity have been established, a treatment plan can be made. Treatment can vary from hand therapy and splinting alone to arthroscopic or open wrist surgery to repair or reconstruct the TFCC.
